Free Mean Kinetic Temperature Calculator
Posted By admin On 04.02.20- Mean Kinetic Temperature Calculator Free Download
- Mean Kinetic Temperature Excel Spreadsheet
- Mean Kinetic Temperature Formula
Monitoring production environments, storage facilities and distribution processes has become an important part of current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) within the biopharmaceutical industry. The FDA and other regulatory bodies have shown increased scrutiny in these areas and require accurate measurement and documentation.As early as 1995, The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) recognized the need for drug storage standards and set out to identify compendial items for which storage and distribution were of special concern. They resolved to have proper storage and shipping instructions included with the compendial item so that the integrity of the product would be maintained until it was received by the patient.What resulted was the adoption of Mean Kinetic Temperature (MKT), a condensation of various proposals, discussions and decades of efforts, that calculates product degradation. In its simplest terms, MKT is a fixed temperature that simulates the effects of temperature variation over a period of time. It differs from other means such as a simple numerical average or arithmetic mean in that higher temperatures are given greater weight in computing the average.
Disproportionate weighting of higher temperature in a temperature series, according to MKT, gives proper recognition to the accelerated rate of thermal degradation of products at higher temperatures. If a specific MKT is exceeded, a second calculation is used to determine the reduction in the product's shelf life, and appropriate actions can then be taken. But MKT is much more than just a number.
It is used to reference temperatures for stability studies, determine a product's acceptable range of storage temperatures, and define 'normal' storage conditions on the product label. MKT: What it is, and What it is NotMean Kinetic Temperature is defined by the USP as 'the single calculated temperature at which the total amount of degradation over a particular period is equal to the sum of the individual degradations that would occur at various temperatures. Thus, MKT may be considered as an isothermal storage temperature that simulates the non-isothermal effects of storage temperature variations.
Mean Kinetic Temperature Calculator Free Download
It is not a simple arithmetic mean. MKT is calculated from temperatures in a storage facility.' It's not a perfect process by any means, and it is not without detractors, but it is the standard. The FDA states in its Code of Federal Regulations, Part 203 that manufacturers, authorized distributors of drugs and their representatives shall store and handle all drug samples under conditions that will maintain their stability, integrity, and effectiveness, and ensure that the drug samples are free of contamination, deterioration and adulteration. This is not possible without the application of MKT.The European Union is more specific. Their Guidance on Good Distribution Practices states, 'The quality system operated by distributors (wholesalers) of medicinal products should ensure that storage conditions are observed at all times, including during transportation.
Products requiring controlled temperature storage should also be transported by appropriately specialized means.' Stability monitoring of medicinal products is an area also addressed by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) in their Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Their final guidance, ICH QA1 (R2), Stability Testing of new Drug Substances and Products, issued in February 2003, has been widely adopted across Europe, Japan and the U.S.
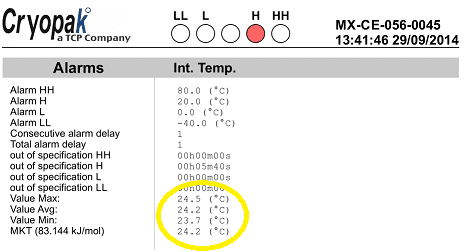
Section 2.1.6 reads in part, 'A drug product should be evaluated under storage conditions that test their thermal stability. The storage conditions and lengths of studies chosen should be sufficient to cover storage, shipment and subsequent use. Data from the accelerated storage conditions, and, if appropriate, the intermediate storage condition can be used to evaluate the effect of short-term excursions outside the label storage conditions (such as during shipping).' Health Canada's Guidelines for Temperature Control of Drug Products during Storage and Transportation, Guide-0069, segregates Warehousing and Storage - 'All drugs should be stored according to conditions described on the label' - and Product Transportation and Products in Transit - 'the transport process and containers should prevent damage and maintain the integrity and quality of the drug products.'
More Than One Way to AverageThere are a number of interpretations of how MKT is achieved, including how many sample values are fed into the formula, whether the minimum and maximum samples are fed into the formula separately (as recommended by the FDA), whether the arithmetic mean is fed into the formula (as recommended by the USP and by the UK MHRA), as well as choices of the stability testing periods, frequencies and whether or not allowances are made for individual datum exceptions. No PanaceaUSP General Chapter Good Storage and Shipping Practices recommends the use of MKT for establishing profiles of storage facilities. They do not, however, reference the use of MKT for determining the environmental effects (including light, humidity, oxygen and temperature) during distribution.
Mean Kinetic Temperature Excel Spreadsheet
Mean Free Path, Molecular Collisions Mean Free PathThe mean free path or average distance between collisions for a gas molecule may be estimated from. Approach is a good visualization - if the molecules have diameter d, then the effective cross-section for collision can be modeled byusing a circle of diameter 2d to represent a molecule's effective collision area while treating the 'target' molecules as point masses. In time t, the circle would sweep out the volume shown and the number of collisions can be estimated from the number of gas molecules that were in that volume.The mean free path could then be taken as the length of the path divided by the number of collisions.The problem with this expression is that the average molecular velocity is used, but the target molecules are also moving. The frequency of collisions depends upon the average of the randomly moving molecules.Reference:Ch. 2.R NaveRefinement of Mean Free PathThe intuitive development of the expression suffers from a significant flaw - it assumes that the 'target' molecules are at rest when in fact they have a high.
What is needed is the average relative velocity, and the calculation of that velocity from the molecular yields the resultwhich revises the expression for the effective volume swept out in time tThe resulting mean free path isThe number of molecules per unit volume can be determined from and the, leading toIt should be noted that this expression for the mean free path of molecules treats them as hard spheres, whereas real molecules are not. For noble gases, the collisions are probably close to being perfectly, so the hard sphere approximation is probably a good one.
Mean Kinetic Temperature Formula
But real molecules may have a and have significant electrical interaction as they approach each other.